Coloboma of the iris
Coloboma of the iris is a hole or defect of the iris of the eye. Most colobomas are present since birth (congenital).
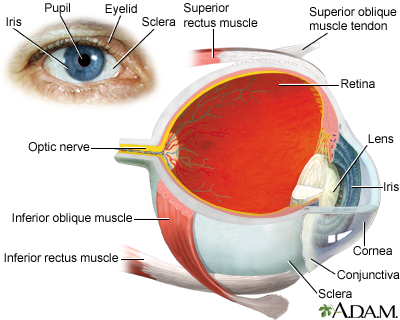
Iris
The iris is the colored part of the eye. It is located between the cornea and lens. The round, central opening of the iris is called the pupil. Ve...

Considerations
Coloboma of the iris can look like a second pupil or a black notch at the edge of the pupil. This gives the pupil an irregular shape. It can also appear as a split in the iris from the pupil to the edge of the iris.
A small coloboma (especially if it is not attached to the pupil) may allow a second image to focus on the back of the eye. This may cause:
- Blurred vision
-
Decreased visual acuity
Decreased visual acuity
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Double vision
- Ghost image
If it is congenital, the defect may include the retina, choroid, or optic nerve.
Retina
The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eyeball. Images that come through the eye's lens are focused on the retina. Th...
Choroid
The choroid is the layer of blood vessels and connective tissue between the white of the eye and retina (at the back of the eye). It is part of the ...

Most colobomas are diagnosed at birth or shortly afterward.
Causes
Most cases of coloboma have no known cause and are not related to other abnormalities. Some are due to a specific genetic defect. A small number of people with coloboma have other inherited developmental problems.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- You notice that your child has what appears to be a hole in the iris or an unusual-shaped pupil.
- Your child's vision becomes blurred or decreased.
In addition to your child, you may also need to see an eye specialist (ophthalmologist).
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will take a medical history and do an exam.
Since the problem is most often diagnosed in infants, knowing about the family history is very important.
The provider will do a detailed eye exam that includes looking into the back of the eye while the eye is dilated. An MRI of the brain, eyes, and connecting nerves may be done if other problems are suspected.
MRI
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
Reviewed By
Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Brodsky MC, Houghton O. Congenital optic disc anomalies. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 9.5.
Freund KB, Sarraf D, Mieler WF, Yannuzzi LA. Congenital and developmental anomalies of the optic nerve. In: Freund KB, Sarraf D, Mieler WF, Yannuzzi LA, eds. The Retinal Atlas. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 15.
National Eye Institute (NIH) website. Coloboma. www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/coloboma. Updated November 15, 2023. Accessed December 6, 2023.
Olitsky SE, Marsh JD. Abnormalities of pupil and iris. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 640.
Porter D. American Academy of Ophthalmology website. What is a coloboma? www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/what-is-coloboma. Accessed December 6, 2023.
Selzer EB, Blain D, Hufnagel RB, Lupo PJ, Mitchell LE, Brooks BP. Review of evidence for environmental causes of uveal coloboma. Surv Ophthalmol. 2022;67(4):1031-1047. PMID: 34979194 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34979194/.
Disclaimer


 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.