Limited range of motion
Limited range of motion is a term meaning that a joint or body part cannot move through its normal range of motion.
-
Considerations
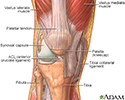
Motion may be limited because of a problem within the joint, swelling of tissue around the joint, stiffness of the ligaments and muscles, or pain.
-
Causes
A sudden loss of range of motion may be due to:
- Dislocation of a joint
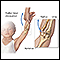
- Fracture of an elbow or other joint
- Infected joint (hip is most common in children)
- Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (in boys 4 to 10 years old)
- Nursemaid elbow, an injury to the elbow joint in young children
- Tearing of certain structures within the joint, such as the meniscus or cartilage
- Lose bodies which have become stuck in the joint
Loss of motion may occur if you damage the bones within a joint. This may happen if you have:
- Broken a joint bone in the past
- Frozen shoulder
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis (a specific form of arthritis)
Brain, nerve, or muscle disorders can damage the nerves, tendons, and muscles, and can cause loss of motion. Some of these disorders include:
- Cerebral palsy (group of disorders that involve brain and nervous system functions)
- Congenital torticollis (wry neck)
- Muscular dystrophy (group of inherited disorders that cause muscle weakness)
- Stroke or brain injury
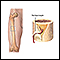
- Volkmann contracture (deformity of the hand, fingers, and wrist caused by injury to the muscles of the forearm)
-
Home Care
Your health care provider may suggest exercises to increase muscle strength and flexibility.
-
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have difficulty moving or extending a joint.
-
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will examine you and ask about your medical history and symptoms.
You may need joint x-rays and spine x-rays. Lab tests may be done.
Physical therapy may be recommended.
References
Debski RE, Patel NK, Shearn JT. Basic concepts in biomechanics. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 2.
Magee DJ, Manske RC. Primary care assessment. Magee DJ, Manske RC, eds. Orthopedic Physical Assessment. 7th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2021:chap 17.