Hyperventilation
Hyperventilation is rapid and deep breathing. It is also called overbreathing, and it may leave you feeling breathless.
Considerations
You breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Excessive breathing creates a low level of carbon dioxide in your blood. This causes many of the symptoms of hyperventilation.
You may hyperventilate from an emotional cause such as during a panic attack. Or, it can be due to a medical problem, such as bleeding or infection.
Panic attack
Panic disorder is a type of anxiety disorder in which you have repeated attacks of intense fear that something bad will happen.
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleYour health care provider will determine the cause of your hyperventilation. Rapid breathing may be due to a medical emergency and you may need to get treated, unless you have had this before and your provider has told you that you can treat it on your own.
If you frequently overbreathe, you may have a medical problem called hyperventilation syndrome.
When you're overbreathing, you might not be aware you're breathing fast and deep. But you'll likely be aware of the other symptoms, including:
- Feeling lightheaded, dizzy, weak, or not able to think straight
- Feeling as if you can't catch your breath
- Chest pain or fast and pounding heartbeat
- Belching or bloating
- Dry mouth
- Muscle spasms in the hands and feet
-
Numbness and tingling in the arms or around the mouth
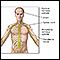
Numbness and tingling
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Problems sleeping
Causes
Emotional causes include:
-
Anxiety and nervousness
Anxiety
Stress is a feeling of emotional or physical tension. It can come from any event or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or nervous. Stres...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Panic attack
- Situations where there is a psychological advantage in having a sudden, dramatic illness (for example, somatization disorder)
Somatization disorder
Somatic symptom disorder (SSD) occurs when a person feels extreme, exaggerated anxiety about physical symptoms. The person has such intense thoughts...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Stress
Stress
Stress is a feeling of emotional or physical tension. It can come from any event or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or nervous. Stres...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Medical causes include:
- Bleeding
- Heart problem such as heart failure or heart attack
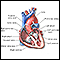
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines (such as an aspirin overdose)
Aspirin overdose
Aspirin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to relieve mild to moderate aches and pains, swelling, and fever. Aspirin overdose occu...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection such as pneumonia or sepsis
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSepsis
Sepsis is an illness in which the body has a severe, inflammatory response to bacteria or other germs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ketoacidosis (usually due to diabetes) and other medical conditions causing excess acid production in the body
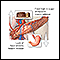
Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening problem that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when the body starts breaking down fat at a r...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung disease such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or pulmonary embolism
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways of the lungs to swell and become narrow. It leads to breathing difficulty such as wheezing, shor...
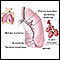 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleChronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePulmonary embolism
A pulmonary embolus is a blockage of an artery in the lungs. The most common cause of the blockage is a blood clot.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pregnancy
- Severe pain
-
Stimulant medicines
Stimulant
Stimulants are chemicals (usually drugs or medicines that increase your heart rate, breathing rate, and brain function. Some stimulants affect only ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Home Care
Your provider will examine you for other causes of your overbreathing.
If your provider has said your hyperventilation is due to anxiety, stress, or panic, there are steps you can take at home. You, your friends, and family can learn techniques to stop it from happening and prevent future attacks.
If you start hyperventilating, the goal is to raise the carbon dioxide level in your blood. This will end most of your symptoms. Ways to do this include:
- Get reassurance from a friend or family member to help you relax your breathing. Words like "you are doing fine," "you are not having a heart attack," and "you are not going to die" are very helpful. It's very important that the person stays calm and uses a soft, relaxed tone.
- To help you get rid of the right amount of carbon dioxide, learn to do pursed lip breathing. This is done by puckering your lips as if you're blowing out a candle, then breathing out slowly through your lips.
Pursed lip breathing
Pursed lip breathing helps you use less energy to breathe. It can help you relax. When you are short of breath, it helps you slow the pace of your ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If you have been diagnosed with anxiety or panic, see a mental health professional to help you understand and treat your condition.
- Learn breathing exercises that help you relax and breathe from your diaphragm and abdomen, rather than from your chest wall.
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation or meditation.
- Exercise regularly.
If these methods alone don't prevent overbreathing, your provider may recommend certain medicines.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You are having rapid breathing for the first time. This may be a medical emergency for which you should be taken to the emergency room right away.
- You are in pain, have a fever, or are bleeding.
- Your hyperventilation continues or gets worse, even with home treatment.
- You also have other symptoms.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms.
Physical exam
During a physical examination, a health care provider checks your body to determine if you do or do not have a physical problem. A physical examinati...
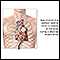
Your breathing will also be checked. If you are not breathing quickly at the time, the provider may try to cause hyperventilation by telling you to breathe in a certain way. The provider will then watch how you breathe and check which muscles you're using to breathe.
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Blood tests for the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in your blood
-
Chest CT scan
Chest CT scan
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
ECG to check your heart
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ventilation/perfusion scan of your lungs to measure breathing and lung circulation
Ventilation/perfusion scan
A pulmonary ventilation/perfusion scan involves two nuclear scan tests to measure breathing (ventilation) and circulation (perfusion) in all areas of...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
X-rays of the chest
X-rays of the chest
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
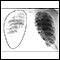 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Reviewed By
Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Braithwaite SA, Wessel AL. Dyspnea. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 21.
Schwartzstein RM, Adams L. Dyspnea. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 36.
Disclaimer



 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.