Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is an infection that occurs from breathing in the spores of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum.
Spores
A spore is a cell that certain fungi, plants (moss, ferns), and bacteria produce. Certain bacteria make spores as a way to defend themselves. Spores...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleCauses
Histoplasmosis occurs throughout the world. In the United States, it is most common in the southeastern, mid-Atlantic, and central states, especially in the Mississippi and Ohio River valleys.
Histoplasma fungus grows as a mold in the soil. You may get sick when you breathe in spores produced by the fungus. Soil that contains bird or bat droppings may have larger amounts of this fungus. The threat is greatest after an old building is torn down, or in caves.
This infection can occur in people with a healthy immune system. Having a weakened immune system increases the risk of getting or reactivating this disease. Very young or very old people, or those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or an organ transplant have more severe symptoms.
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...

Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
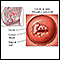
People with long-term (chronic) lung disease (such as emphysema and bronchiectasis) are also at higher risk for a more severe infection.
Emphysema
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
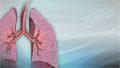
Bronchiectasis
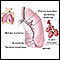
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which the large airways in the lungs are damaged. This causes the airways to become permanently wider. Bronchiectasis...
Symptoms
Most people have no symptoms, or only have a mild, flu-like illness.
If symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Fever and chills
Chills
Chills refers to feeling cold after being in a cold environment. The word can also refer to an episode of shivering along with paleness and feeling ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cough and chest pain that gets worse when breathing in
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Joint pain
-
Mouth sores
Mouth sores
There are different types of mouth sores. They can occur anywhere in the mouth including bottom of the mouth, inner cheeks, gums, lips, and tongue....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Red skin bumps, most often on the lower legs
The infection may be active for a short period of time, and then the symptoms go away. Sometimes, the lung infection may become chronic. Symptoms include:
- Chest pain and shortness of breath
- Cough, possibly coughing up blood
- Fever and sweating
In a small number of people, especially in those with a weakened immune system, histoplasmosis spreads throughout the body. This is called disseminated histoplasmosis. In response to the infection irritation and swelling (inflammation) occur in parts of the body. Symptoms may include:
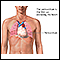
- Chest pain from inflammation of the sac-like covering around the heart (pericarditis)
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headache and neck stiffness from swelling of the membranes covering of the brain and spinal cord (meningitis)
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High fever
Exams and Tests
Histoplasmosis is diagnosed by:
-
Biopsy of the lung, skin, liver, or bone marrow
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
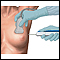 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urine or blood tests to detect histoplasma proteins or antibodies
Blood
Histoplasma complement fixation is a blood test that checks for infection by a fungus called Histoplasma capsulatum (H capsulatum), which causes the ...
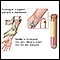 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cultures of the blood, urine, or sputum (this test provides the clearest diagnosis of histoplasmosis, but results can take 6 weeks)
Cultures of the blood
A blood culture is a laboratory test to check for bacteria or other germs in a blood sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleUrine
A urine culture is a lab test to check for bacteria or other germs in a urine sample. It can be used to check for a urinary tract infection in adults...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSputum
Routine sputum culture is a laboratory test that looks for germs that cause infection. Sputum is the material that comes up from air passages when y...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
To help diagnose this condition, your health care provider may do a:
-
Bronchoscopy (test that uses a viewing scope inserted into the lung airway to check for signs of infection)
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
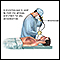 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest CT scan
Chest CT scan
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
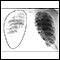 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Spinal tap to look for signs of infection in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Spinal tap
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
In otherwise healthy people, this infection usually goes away without treatment.
If you are sick for more than 1 month or are having trouble breathing, your provider may prescribe medicine. The main treatment for histoplasmosis is antifungal medicines.
- Antifungals may need to be given through a vein, depending on the form or stage of the disease.
- Some of these medicines can have side effects.
- Long-term treatment with antifungal medicines may be needed for up to 1 to 2 years.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook depends on how severe the infection is, and your general health condition. Some people get better without treatment. An active infection will usually go away with antifungal medicine. But, the infection may leave scarring inside the lung.
The death rate is higher for people with untreated disseminated histoplasmosis who have a weakened immune system.
Possible Complications
Scarring in the chest cavity may put pressure on the:
- Major blood vessels carrying blood to and from the heart
- Heart
- Esophagus (food pipe)
- Lymph nodes
Enlarged lymph nodes in the chest may press on body parts such as the esophagus and blood vessels of the lungs.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you live in an area where histoplasmosis is common and you develop:
- Flu-like symptoms
- Chest pain
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
While there are many other illnesses that have similar symptoms, you may need to be tested for histoplasmosis.
Prevention
Histoplasmosis may be prevented by reducing your exposure to dust in chicken coops, bat caves, and other high-risk locations. Wear masks and other protective equipment if you work in or go into these environments.
Reviewed By
Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Deepe GS. Histoplasma capsulatum (histoplasmosis). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 263.
Thompson GR, Miceli MH. Endemic mycoses. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 308.
Disclaimer





 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.